ABSTRACT
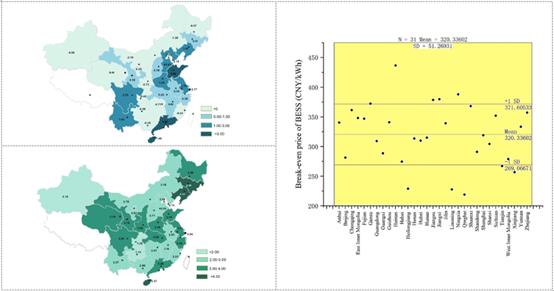
As the development of distributed solar photovoltaics (DSPV), battery energy storage systems are growing in popularity to promote the performance of DSPV, for both mitigating the impact on the grid and increasing the economic performance. In the meantime, reused batteries retired from electric vehicles provide another option for energy storage systems. In this paper, the economic performance evaluated by net present value of DSPV with reused batteries as energy storage systems (RBESS) is studied at the provincial level in China, so as to depict a comprehensive understanding of the current DSPV status and the development potential of RBESS in China. Instead of only focusing on the rosle of increasing the percentage of self-consumption (Model 1), a combined usage strategy of RBESS (Model 2) is also proposed. Moreover, the residual value of lithium-ion batteries is taken into consideration in this paper. Our results show that for the residential sector, only a small number of areas can benefit from RBESS under Model 2, while none can benefit under Model 1. Only when the price of RBESS decreases to 200 CNY/kWh, the profitability could be nationwide. However, for the commercial and industrial sector, the performance of RBESS is much better. In the majority of areas, integrating RBESS with DSPV is already profitable.
KEYWORDS
Distributed solar photovoltaics; Reused batteries; Net present value; Energy storage systems; Self-consumption; Load-leveling
JCR CLASSIFICATION
Q1
Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2019.03.048
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.05.001
