ABSTRACT
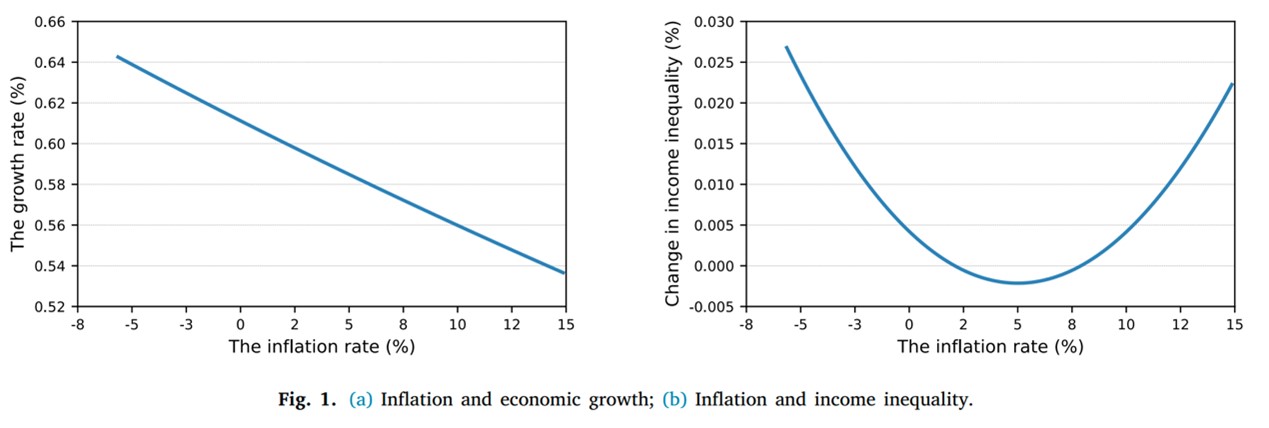
We explore the effects of monetary policy on innovation and income inequality in a scale-invariant endogenous growth model with heterogeneous households and a cash-in-advance (CIA) constraint on research and development investment. Household heterogeneity arises from unequal distributions of wealth and skill, giving rise to interest and labor income inequalities, respectively. We find that inflation unambiguously reduces innovation and economic growth, whereas its impact on income inequality can be positive, negative, or U-shaped. The relationship between inflation and income inequality depends on the relative dominance of wealth heterogeneity to skill heterogeneity and how the ratio of interest income to labor income responds to inflation. The model is calibrated to the US economy, and the numerical results support these implications on income inequality.
KEYWORDS
Income inequality, Inflation, Wealth and skill heterogeneity, Endogenous economic growth
JCR CLASSIFICATION
Q1
JEL CLASSIFICATION
D31;O30;O40;E41
Economic Modelling
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.econmod.2023.106193
